142. Linked List Cycle II
Given the head of a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail’s next pointer is connected to (0-indexed). It is -1 if there is no cycle. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
Do not modify the linked list.
快慢指针。快指针的移动速度是慢指针的两倍。
设环外长度为a,b是快指针和慢指针相遇的位置,c是环中剩余位置。
可以由此得到公式a + (n + 1)b + nc = 2(a + b),也就是a = c + (n - 1)(b + c)
由于(b + c)是环的长度。因此,当两个指针相遇时,在头部设置一个新节点。慢指针和新指针将在循环入口处相遇,此时返回节点。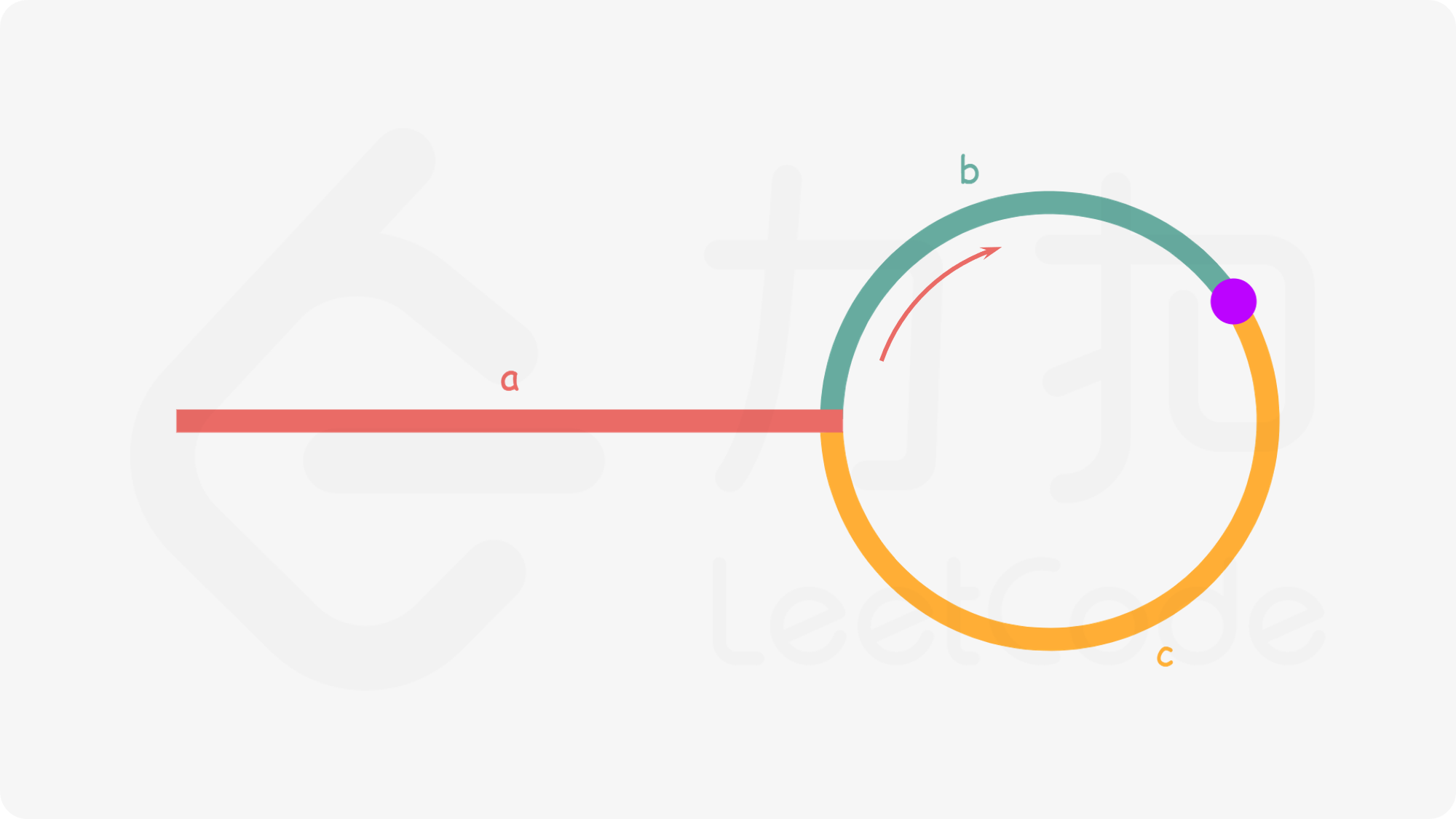
1 | /** |
哈希表,递归并将节点加入哈希集合,如果重复则返回节点,反之返回null。
1 | /** |
142. Linked List Cycle II
https://xuanhe95.github.io/2022/04/25/142-Linked-List-Cycle-II/
